4 advantages (and 1 disadvantage) of desiccant dehumidifiers
Feb 20, 2025High humidity can be unpleasant. If you're choosing a dehumidifier, this brief overview of the advantages and disadvantages...
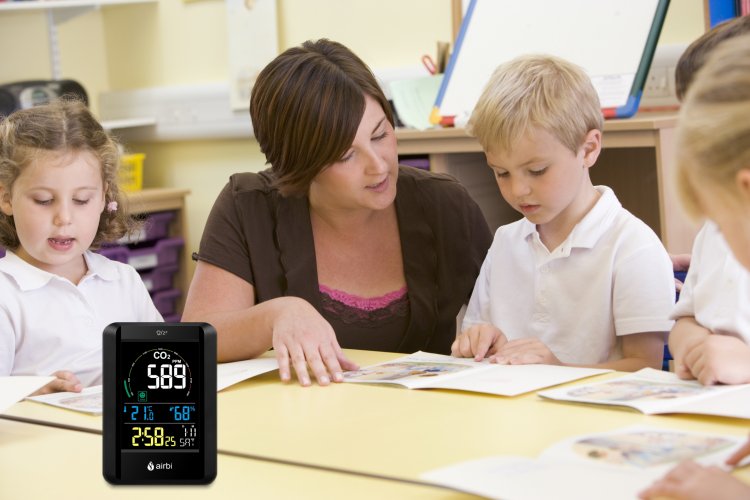
Do you suffer from headaches or respiratory irritation during your stay indoors? The cause of these problems may be sick building syndrome caused by elevated levels of volatile organic compounds. Read about how VOCs get into the air, what health effects they can have, and what helps fight them.
Volatile organic compounds (VOCs) are gaseous substances that evaporate very quickly into the air, hence their name. It is a group of about 200 substances with different properties that often have very negative consequences for our body.
VOCs arise from very different sources. These are either of natural origin or man-made. Natural resources are, for example, products of material exchange, rotting and decomposition processes of natural materials such as wood or oil. Biogenic volatile organic compounds are most often emitted by plants, animals or microorganisms and are very diverse.
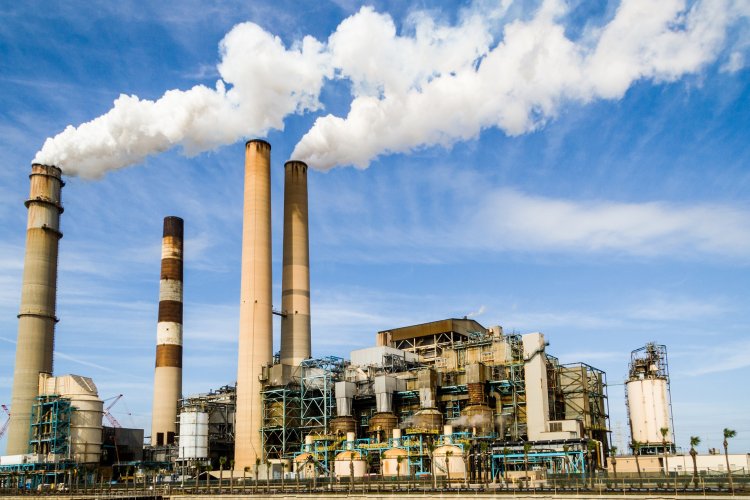
Anthropogenic VOCs, i.e. those created by human activity, are contained in many everyday objects such as furniture and decorative materials, hobby products and cleaning products. In addition, VOCs are produced during incomplete combustion or as a by-product of industrial processes. Synthetic sources are, for example, vapors from building materials (varnishes, paints, carpets, insulating materials), solvents or cleaning agents or cosmetics.

Natural cleaning agents are much more suitable than chemical ones
Volatile organic compounds react with nitrogen oxides in the presence of sunlight. This process creates hazardous substances that are potentially dangerous to human health or the ozone layer in the atmosphere. Even at room temperatures, VOCs turn to gas and are released into the room air. This occurs when solvents or liquid fuels evaporate, or when liquid or pasty products dry out. Easier to identify is a leak from products such as glue or paint. More problematic are the so-called material emissions, which are constantly released by some plastics. Typical examples are various plasticizers, solvents, antioxidants or fragrances and flame retardants.
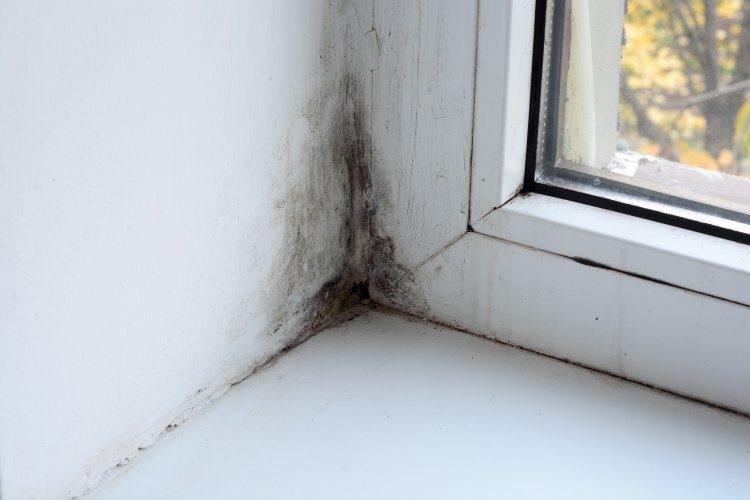
As we Central Europeans spend most of our time indoors, elevated VOC levels are of greater health concern. Especially since indoors, the distance to VOC sources is usually smaller. Particularly high levels of VOC pollution occur immediately after construction or extensive renovation, when release rates are strongest.

New synthetic materials are one of the largest sources of VOCs
An increased concentration of VOCs manifests itself as a bothersome smell. This can cause a change in the perception of smell and taste as well as irritation of the eyes and mucous membranes. Other common effects are exhaustion, lack of concentration, dry skin, eczema or headaches.
With long-term exposure to VOCs, it is very likely that you will suffer chronic effects, to a great extent. Cancer growth, mutations in the genotype or problems with fertility can be the result. Infants and young children, who have not yet developed a sufficiently strong defense system, are particularly susceptible to VOCs.

The Airbi SPRING WiFi air purifier quickly rids you of dangerous VOCs